How do you define industrial automation?
By definition, industrial automation refers to the use of a programmable logic controller (PLC) to fully automate a production line. In other words, it's a set of industrial machines and systems that carry out the process with virtually no human intervention.
It may, for example, involve tasks such as assembling products, packaging items, running production recipes or carrying out quality checks.
The operators' intervention is limited to supervising and monitoring the general smooth running. They can also modify instructions and provide contextual feedback for operator stations.
What are the basics of industrial automation?
Today, industrial automation is made possible by a variety of technologies, including:
programmable logic controllers (PLCs) are specialized processors used to control industrial machines and processes. PLCs can be programmed using specific programming languages, such as ladder logic, Grafcet, CFC, etc.
They are equipped with microcontrollers and software that enable them to perform advanced tasks, such as data analysis or local decision-making. Smart sensors can also communicate directly with control systems, enabling more advanced process automation.
They use cameras and image processing software to detect and inspect parts or industrial products. These systems enable advanced automation of quality control and part sorting tasks.
These are programmable machines that can perform tasks that are repetitive or dangerous for humans. Industrial robots are used, for example, for assembly, palletizing, machine loading/unloading, etc.
Control and data acquisition systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes. These systems can be used to automate tasks such as machining parts, setting temperatures, etc.
Allows operators to interact with automated systems. This can include tasks such as starting and stopping processes, setting parameters and viewing data.
What are the challenges of industrial automation?
Industrial automation has evolved considerably over the decades to become a key element of modern industrial production.
Automation enables reproducing repetitive tasks automatically and without human presence, thus reducing the drudgery of certain operations.
It has been used in factories for centuries, but the term "industrial automation" only appeared at the beginning of the 20th century.
-
First generation (1950s-60s):
Automation began with the use of electromechanical relays to control machines and processes.
-
Second generation (1970s-80s):
The introduction of programmable logic controllers marked a major advance in industrial automation. These were specialized computers capable of controlling more complex and diverse processes.
-
Third generation (years 1990-2000):
Automation extended to distributed process control systems and computerized manufacturing control systems. These advanced IT systems enabled real-time monitoring, control and optimization of industrial processes.
-
Fourth generation (years 2010-present):
the introduction of Internet of Things (IoT) technology and data analytics enabled even greater automation. IoT sensors can monitor machines and processes in real time, providing valuable data for process analysis and optimization. Here, human-machine interaction is minimal.
In addition to the issues surrounding automated systems, industrial control and automatic regulation are also essential for most industrial processes. These terms refer to all the methods and technologies used to monitor, regulate and control production processes.
In short, industrial control and automatic regulation are key concepts for maintaining efficient, high-quality production processes. Their combination enables companies to improve their efficiency, quality and profitability in the marketplace.
In the coming years, the industrial automation market will continue to evolve, particularly with the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI). It will need to respond to multiple economic, social and environmental challenges.
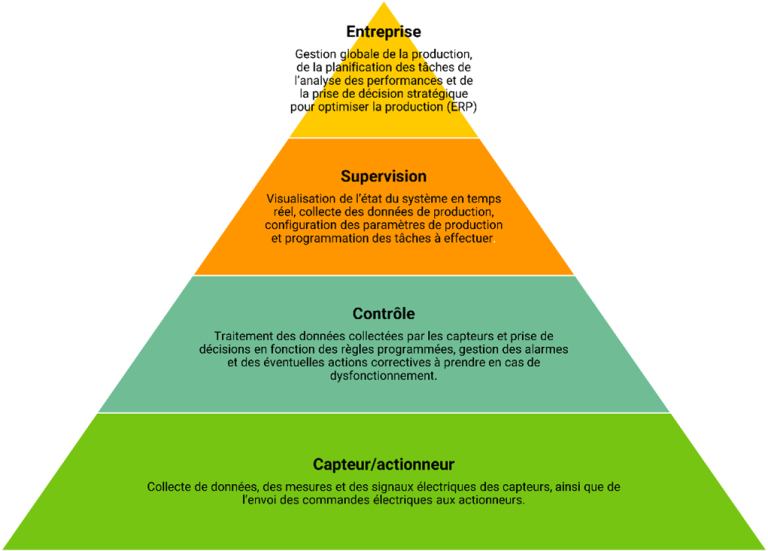
What are the levels of industrial automation?
Industrial automation levels are generally divided into four levels, each corresponding to a different type of function or task:
To sum up, the levels of industrial automation make it possible to separate the tasks and responsibilities associated with industrial production into different strata. Each with its own specific and complementary functionalities. The higher levels are more oriented towards the overall management of production, while the lower levels are more focused on the control and execution of automated tasks.
Why automate your industrial production?
By modifying your existing data acquisition and processing processes through system integration, you'll discover a new way of controlling your production. The benefits are manifold:
- Intuitive system for operators
- Compliance with lean manufacturing
- Regulation of production flows
- Monitoring and control of production inmonitoring and control
- Standardization of automated identification systems
- More accurate demand forecasts
- Cost reduction
- Flexibility
.
Why use an industrial automation company?
All organizations, whatever their industrial sector, have a vested interest in getting to grips with the subject of automation.
In fact, to produce quickly and keep up with the competition, factories need to adopt new production styles, new processes. Operators and technicians will also have to adapt as best they can to a more automated and connected production environment.
To organize this kind of transformation, calling on an expert company in automation and industrial systems proves to be a useful ally for a production site. It can bring many benefits:
How do you choose a company with expertise in industrial automation?
Selecting an automation company can be a complex process, requiring careful evaluation of several factors. Elements to consider when selecting an industrial automation integrator include: skills, range of services offered, cost of service, flexibility and customer service.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can find a company that will meet your automation needs efficiently and cost-effectively.
You have an industrial automation project and are looking for an automation integrator?
Our experts master the entire value chain, from control to information systems. They offer turnkey solutions and support you from feasibility study to commissioning.